Yellow Birch or Grey Birch Tree
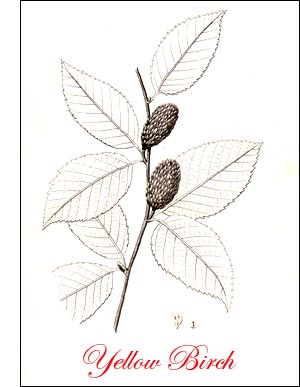 Yellow Birch, Grey Birch (Betula lutea, Michx.)-Medium sized tree, 50 to 75 feet, rarely l00 feet high, with broad, round top with slender, drooping branchlets ending in fine, leafy spray. Bark aromatic, bitter, dark grey, rough, with deep, irregular furrows, and thick plates; younger stems silvery yellow, peeling horizontally in ribbons; remnants of this lustrous bark seen on plates of old trunks; twigs pubescent the first season. Wood reddish brown, pale, heavy, hard, strong, close grained, satiny. Buds pointed, 4 inch long, brown, shiny. Leaves ovate, 3 to 4 inches long, sharply and doubly serrate, pointed, oblique at base; veins conspicuous, hairy beneath, midrib stout; petiole short, hairy; colour dull dark green, with yellow-green lining; autumn, pale yellow.
Yellow Birch, Grey Birch (Betula lutea, Michx.)-Medium sized tree, 50 to 75 feet, rarely l00 feet high, with broad, round top with slender, drooping branchlets ending in fine, leafy spray. Bark aromatic, bitter, dark grey, rough, with deep, irregular furrows, and thick plates; younger stems silvery yellow, peeling horizontally in ribbons; remnants of this lustrous bark seen on plates of old trunks; twigs pubescent the first season. Wood reddish brown, pale, heavy, hard, strong, close grained, satiny. Buds pointed, 4 inch long, brown, shiny. Leaves ovate, 3 to 4 inches long, sharply and doubly serrate, pointed, oblique at base; veins conspicuous, hairy beneath, midrib stout; petiole short, hairy; colour dull dark green, with yellow-green lining; autumn, pale yellow. Flowers before leaves in April; staminate catkins, 3 to 4 inches long, brown above, yellow below the middle; pistillate catkins 2/3 inch long, reddish green, hairy. Fruits: cones oblong or ovoid, stout, 1 inch long, erect, scales 3-lobed, narrow, tapering, hairy; nut oval, with narrow wings. Preferred habitat, rich, moist uplands. Distribution, Newfoundland south to Delaware, North Carolina and Tennessee; west to Minnesota. Uses: A desirable ornamental tree, but rarely planted. Wood valuable for implements, furniture, wheel hubs, button moulds, boxes, and for fuel.
The bark again gives the name to a large birch that grows here and there in the forests of the Northern States. -1 he fringed and tattered outer bark, dingy grey with pearly lustre, and showing gleams of gold at every rent, is unlike the other birches. The twigs are aromatic, but not to compare with the black birch. In grace and lustiness the two trees are well matched. The yellow birch leads in size, of its catkins, fruiting cones, and the tree itself. The leaves are not larger, but they are more distinctly toothed, the double serrations being regular and clear cut.
Yellow Birch Tree picture